nf-core/bactmap
A mapping-based pipeline for creating a phylogeny from bacterial whole genome sequences
Introduction
This document describes the output produced by the pipeline. Most of the plots are taken from the MultiQC report, which summarises results at the end of the pipeline.
The directories listed below will be created in the results directory after the pipeline has finished. All paths are relative to the top-level results directory.
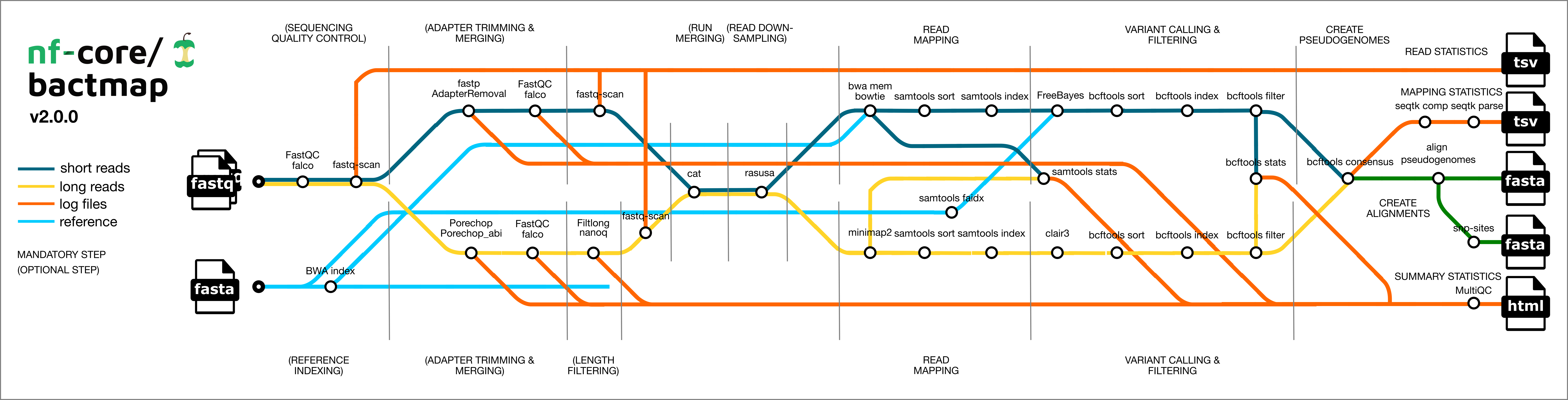
Pipeline overview
The pipeline is built using Nextflow and processes data using the following steps:
- SAMtools faidx - Indexing of reference genome
- FastQC - Raw read QC
- fastq-scan - Summary statistics for fastq files
- falco - Alternative to FastQC for raw read QC
- fastp - Adapter trimming for Illumina data
- AdapterRemoval - Adapter trimming for Illumina data
- Porechop - Adapter removal for Oxford Nanopore data
- Porechop_ABI - Adapter removal for Oxford Nanopore data
- Filtlong - Quality trimming and filtering for Nanopore data
- Nanoq - Quality trimming and filtering for Nanopore data
- Run Merging - Merging of reads from multiple sequencing runs
- Analysis Ready Reads - Optional results directory containing the final processed reads used as input for subsampling.
- Rasusa - Subsampling of reads
- read_stats - Summarise read statistics pre- and post-processing
- Bowtie2 - Mapping for Illumina reads
- BWA MEM2 - Mapping for Illumina reads
- minimap2 - Mapping for Nanopore reads
- SAMtools sort - Sorting of bam files
- SAMtools stats - Statistics from mapping
- FreeBayes - Variant calling for Illumina reads
- Clair3 - Variant calling for Nanopore reads
- BCFtools filter - Filtering of variants
- BCFtools stats - Statistics from variant calling
- BCFtools consensus - Convert filtered bcf to pseudogenome fasta
- seqtk - Summarise mapping statistics
- Align pseudogenomes - Create alignment from pseudogenomes
- SNP-sites - Extract variant sites from alignment
- MultiQC - Aggregate report describing results and QC from the whole pipeline
- Pipeline information - Report metrics generated during the workflow execution
SAMtools faidx
SAMtools faidx is used to index the reference genome. The index file is required for downstream mapping steps.
Output files
samtools/faidx<reference_genome>.fai: Index file for the reference genome<reference_genome>.gzi: Gzip index file for the reference genome
FastQC or Falco
Output files
{fastqc,falco}/- {raw,preprocessed}
*html: FastQC or Falco report containing quality metrics in HTML format.*.txt: FastQC or Falco report containing quality metrics in TXT format.*.zip: Zip archive containing the FastQC report, tab-delimited data file and plot images (FastQC only).
- {raw,preprocessed}
FastQC gives general quality metrics about your sequenced reads. It provides information about the quality score distribution across your reads, per base sequence content (%A/T/G/C), adapter contamination and overrepresented sequences. For further reading and documentation see the FastQC help pages.
If preprocessing is turned on, nf-core/bactmap runs FastQC/Falco twice -once before and once after adapter removal/read merging, to allow evaluation of the performance of these preprocessing steps. Note in the General Stats table, the columns of these two instances of FastQC/Falco are placed next to each other to make it easier to evaluate. However, the columns of the actual preprocessing steps (i.e, fastp, AdapterRemoval, and Porechop) will be displayed after the two FastQC/Falco columns, even if they were run ‘between’ the two FastQC/Falco jobs in the pipeline itself.
Falco produces identical output to FastQC but in the falco/ directory.
fastq-scan
Output files
fastqscan/raw/*.json: JSON formatted file of summary statistics for input fastq files.processed/*.json: JSON formatted file of summary statistics for processed fastq files.
summaries/raw_fastq-scan_summary.tsv: Final summary tsv file of sequencing statistics for analysis ready fastq files for all samples.processed_fastq-scan_summary.tsv: Final summary tsv file of sequencing statistics for merged, subsampled fastq files for all samples.
fastq-scan is a tool for generating FASTQ summary statistics in JSON format.
fastp
fastp is a FASTQ pre-processing tool for quality control, trimmming of adapters, quality filtering and other features.
It is used in nf-core/bactmap for adapter trimming of short-reads.
Output files
fastp/<sample_id>.fastp.fastq.gz: File with the trimmed unmerged fastq reads.<sample_id>.merged.fastq.gz: File with the reads that were successfully merged.<sample_id>.*{log,html,json}: Log files in different formats.
By default nf-core/bactmap will only provide the <sample_id>.fastp.fastq.gz file if fastp is selected. The file <sample_id>.merged.fastq.gz will be available in the output folder if you provide the argument --shortread_qc_mergepairs (optionally retaining un-merged pairs when in combination with --shortread_qc_includeunmerged).
You can change the default value for low complexity filtering by using the argument --shortread_complexityfilter_fastp_threshold.
AdapterRemoval
AdapterRemoval searches for and removes remnant adapter sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) data and (optionally) trims low quality bases from the 3’ end of reads following adapter removal. It is popular in the field of palaeogenomics. The output logs are stored in the results folder, and as a part of the MultiQC report.
Output files
adapterremoval/<sample_id>.settings: AdapterRemoval log file containing general adapter removal, read trimming and merging statistics<sample_id>.collapsed.fastq.gz- read-pairs that merged and did not undergo trimming (only when--shortread_qc_mergepairssupplied)<sample_id>.collapsed.truncated.fastq.gz- read-pairs that merged underwent quality trimming (only when--shortread_qc_mergepairssupplied)<sample_id>.pair1.truncated.fastq.gz- read 1 of pairs that underwent quality trimming<sample_id>.pair2.truncated.fastq.gz- read 2 of pairs that underwent quality trimming (and could not merge if--shortread_qc_mergepairssupplied)<sample_id>.singleton.truncated.fastq.gz- orphaned read pairs where one of the pair was discarded<sample_id>.discard.fastq.gz- reads that were discarded due to length or quality filtering
By default nf-core/bactmap will only provide the .settings file if AdapterRemoval is selected.
You will only find the .fastq files in the results directory if you provide --save_preprocessed_reads. If this is selected, you may receive different combinations of .fastq files for each sample depending on the input types - e.g. whether you have merged or not, or if you’re supplying both single- and paired-end reads. Alternatively, if you wish only to have the ‘final’ reads that go into subsampling (i.e., that may have additional processing), do not specify this flag but rather specify --save_analysis_ready_fastqs, in which case the reads will be in the folder analysis_ready_reads.
The resulting .fastq files may not always be the ‘final’ reads that go into subsampling, if you also run other steps such as run merging etc..
Porechop
Porechop is a tool for finding and removing adapters from Oxford Nanopore reads. Adapters on the ends of reads are trimmed and if a read has an adapter in its middle, it is considered a chimeric and it chopped into separate reads.
Output files
porechop/<sample_id>.log: Log file containing trimming statistics<sample_id>.fastq.gz: Adapter-trimmed file
The output logs are saved in the output folder and are part of MultiQC report.You do not normally need to check these manually.
You will only find the .fastq files in the results directory if you provide --save_preprocessed_reads. Alternatively, if you wish only to have the ‘final’ reads that go into subsampling (i.e., that may have additional processing), do not specify this flag but rather specify --save_analysis_ready_fastqs, in which case the reads will be in the folder analysis_ready_reads.
We do not recommend using Porechop if you are already trimming the adapters with ONT’s basecaller Guppy.
Porechop_ABI
Porechop_ABI is an extension of Porechop. Unlike Porechop, Porechop_ABI does not use any external knowledge or database for the adapters. Adapters are discovered directly from the reads using approximate k-mers counting and assembly. Then these sequences can be used for trimming, using all standard Porechop options. The software is able to report a combination of distinct sequences if a mix of adapters is used. It can also be used to check whether a dataset has already been trimmed out or not, or to find leftover adapters in datasets that have been previously processed with Guppy.
Output files
porechop_abi/<sample_id>.log: Log file containing trimming statistics<sample_id>.fastq.gz: Adapter-trimmed file
The output logs are saved in the output folder and are part of MultiQC report.You do not normally need to check these manually.
You will only find the .fastq files in the results directory if you provide --save_preprocessed_reads. Alternatively, if you wish only to have the ‘final’ reads that go into subsampling (i.e., that may have additional processing), do not specify this flag but rather specify --save_analysis_ready_fastqs, in which case the reads will be in the folder analysis_ready_reads.
Filtlong
Filtlong is a quality filtering tool for long reads. It can take a set of small reads and produce a smaller, better subset.
Output files
filtlong/<sample_id>_filtered.fastq.gz: Quality or long read data filtered file<sample_id>_filtered.log: log file containing summary statistics
You will only find the .fastq files in the results directory if you provide --save_preprocessed_reads. Alternatively, if you wish only to have the ‘final’ reads that go into subsampling (i.e., that may have additional processing), do not specify this flag but rather specify --save_analysis_ready_fastqs, in which case the reads will be in the folder analysis_ready_reads.
We do not recommend using Filtlong if you are performing filtering of low quality reads with ONT’s basecaller Guppy.
Nanoq
nanoq is an ultra-fast quality filtering tool that also provides summary reports for nanopore reads.
Output files
nanoq/<sample_id>_filtered.fastq.gz: Quality or long read data filtered file<sample_id>_filtered.stats: Summary statistics report
You will only find the .fastq files in the results directory if you provide --save_preprocessed_reads. Alternatively, if you wish only to have the ‘final’ reads that go into subsampling (i.e., that may have additional processing), do not specify this flag but rather specify --save_analysis_ready_fastqs, in which case the reads will be in the folder analysis_ready_reads.
Run Merging
nf-core/bactmap offers the option to merge FASTQ files of multiple sequencing runs or libraries that derive from the same sample, as specified in the input samplesheet.
This is the last possible preprocessing step, so if you have multiple runs or libraries (and run merging turned on), this will represent the final reads that will go into subsampling steps.
Output files
run_merging/<sample_id>.fastq.gz: Concatenated FASTQ files on a per-sample basis
Note that you will only find samples that went through the run merging step in this directory. For samples that had a single run or library will not go through this step of the pipeline and thus will not be present in this directory.
This directory and its FASTQ files will only be present if you supply --save_runmerged_reads. Alternatively, if you wish only to have the ‘final’ reads that go into subsampling (i.e., that may have additional processing), do not specify this flag but rather specify --save_analysis_ready_fastqs, in which case the reads will be in the folder analysis_ready_reads.
Analysis Ready Reads
This optional results directory will only be present in the pipeline results when supplying --save_analysis_ready_fastqs.
Output files
analysis_ready_fastqs/<sample_id>_{fq,fastq}.gz: Final reads that underwent preprocessing and were sent for subsampling.
The results directory will contain the ‘final’ processed reads used as input for subsampling. It will only include the output of the last step of any combinations of preprocessing steps that may have been specified in the run configuration. For example, if you perform the read QC, the final reads that are sent to subsampling are the post-QC processed ones - those will be the ones present in this directory.
If you turn off all preprocessing steps, then no results will be present in this directory. This happens independently for short- and long-reads i.e. you will only have FASTQ files for short reads in this directory if you skip all long-read preprocessing.
Rasusa
The rasusa software is used to subsample reads to a depth cutoff of a default of 100 (unless the --subsampling_off flag is set)
Output files
rasusa/<sample_id>.fastq.gzsubsampled fastq files
read_stats
Output files
read_stats/<sample_id>.tsv: Pre- and post-processing sequence statistics.
summariesread_stats_summary.tsv: Final summary tsv file of pre- and post-processing sequence statistics for all samples.
Bowtie2
Bowtie 2 is an ultrafast and memory-efficient tool for aligning sequencing reads to long reference sequences. It is particularly good at aligning reads of about 50 up to 100s or 1,000s of characters, and particularly good at aligning to relatively long (e.g. mammalian) genomes.
It is used with nf-core/bactmap to map short reads to the reference genome.
Output files
bowtie2/build/*.bt2: Bowtie2 indices of reference genome
align/<sample_id>.log: log file about the mapped reads
While there is a dedicated section in the MultiQC HTML for Bowtie2, these values are not displayed by default in the General Stats table. Rather, alignment statistics to host genome is reported via samtools stats module in MultiQC report.
BWA MEM2
BWA MEM2 is a fast and accurate aligner for mapping short reads to reference sequences.
It is used with nf-core/bactmap to map short reads to the reference genome.
Output files
bwamem2/index/*.amb: BWA-MEM2 indices of reference genome*.ann: BWA-MEM2 indices of reference genome*.bwt: BWA-MEM2 indices of reference genome*.pac: BWA-MEM2 indices of reference genome*.sa: BWA-MEM2 indices of reference genome
While there is a dedicated section in the MultiQC HTML for BWA-MEM2, these values are not displayed by default in the General Stats table. Rather, alignment statistics to host genome is reported via samtools stats module in MultiQC report.
minimap2
minimap2 is an alignment tool suited to mapping long reads to reference sequences.
It is used with nf-core/bactmap to map short reads to the reference genome.
Output files
minimap2/build/*.mmi2: minimap2 indices of reference genome.
minimap2 is not yet supported as a module in MultiQC and therefore there is no dedicated section in the MultiQC HTML. Rather, alignment statistics to host genome is reported via samtools stats module in MultiQC report.
SAMtools sort
SAMtools sort is used to sort the BAM files generated by the mapping steps. The sorted BAM files are used for downstream variant calling.
Output files
-
samtools/sort/<sample_id>.sorted.bam: Sorted BAM file containing reads that aligned against the user-supplied reference genome as well as unmapped reads<sample_id>.sorted.bam.bai: Index file for the sorted BAM file
SAMtools stats
SAMtools stats collects statistics from a .sam, .bam, or .cram alignment file and outputs in a text format.
Output files
samtools/stats/<sample_id>.sorted.bam.stats: File containing samtools stats output.<sample_id>.sorted.bam.flagstat: Flagstat file for the sorted BAM file<sample_id>.sorted.bam.idxstats: Index statistics file for the sorted BAM file
In most cases you do not need to check this file, as it is rendered in the MultiQC run report.
FreeBayes
FreeBayes is a haplotype-based variant detector designed to find SNPs, indels, and complex variants in short-read data. It is used with nf-core/bactmap to call variants from short-read data.
Output files
freebayes/variants/<sample_id>.vcf.gz: VCF file containing variants<sample_id>.vcf.gz.tbi: Index file for the VCF file
Clair3
Clair3 is a variant caller for long-read data. It is used with nf-core/bactmap to call variants from long-read data.
Output files
clair3/variants/<sample_id>.vcf.gz: VCF file containing variants<sample_id>.vcf.gz.tbi: Index file for the VCF file<sample_id>.vcf.gz.stats: Statistics file for the VCF
BCFtools filter
The BCFtools software is used to call and filter variants found within the bam files.
Output files
variants/filtered<sample_id>.vcf.gzfiltered vcf files containing variants
BCFtools stats
BCFtools stats is used to generate statistics from the variant calling step. The output is a summary of the variants found in the vcf files.
Output files
bcftools/stats/<sample_id>.statsBCFtools stats output files<sample_id>.tsvBCFtools stats summary files
BCFtools consensus
The filtered vcf files are converted to a pseudogenome.
Output files
pseudogenomes/<sample_id>.faspseudogenome with a base at each position of the reference sequence
seqtk
The seqtk tool is used to identify the number of mapped bases within the pseudogenome fasta files.
Output files
seqtk/<sample_id>.tsvtsv with base count and distribution for each pseudogenome
summariesmapping_summary.tsvSummary of seqtk output for all samples
Align pseudogenomes
Only those pseudogenome fasta files that have a non-ACGT fraction less than the threshold specified will be included in the aligned_pseudogenomes.fas file. Those failing this will be reported in the low_quality_pseudogenomes.tsv file.
Output files
pseudogenomes/aligned_pseudogenomes.fasalignment of all sample pseudogenomes and the reference sequencelow_quality_pseudogenomes.tsva tab separated file of the samples that failed the non-ACGT base threshold
SNP-sites
Non-informative constant sites are removed from the alignment using snp-sites
Output files
snpsites/constant.sites.txtA file with the number of constant sites for each basefiltered_alignment.fasAlignment with only informative positions (those positions that have at least one alternative variant base)
MultiQC
Output files
multiqc/multiqc_report.html: a standalone HTML file that can be viewed in your web browser.multiqc_data/: directory containing parsed statistics from the different tools used in the pipeline.multiqc_plots/: directory containing static images from the report in various formats.
MultiQC is a visualization tool that generates a single HTML report summarising all samples in your project. Most of the pipeline QC results are visualised in the report and further statistics are available in the report data directory.
Results generated by MultiQC collate pipeline QC from supported tools e.g. FastQC. The pipeline has special steps which also allow the software versions to be reported in the MultiQC output for future traceability. For more information about how to use MultiQC reports, see http://multiqc.info.
All tools in bactmap supported by MultiQC will have a dedicated section showing summary statistics of each tool based on information stored in log files.
You can expect in the MultiQC reports either sections and/or general stats columns for the following tools:
- fastqc
- fastp
- adapterremoval
- porechop
- porechop_abi
- filtlong
- nanoq
- samtools stats
- bcftools stats
The ‘General Stats’ table by default will only show statistics referring to pre-processing steps, and will not display statistics from mapping and variant calling, unless turned on by the user within the ‘Configure Columns’ menu or via a custom MultiQC config file (--multiqc_config).
Pipeline information
Output files
pipeline_info/- Reports generated by Nextflow:
execution_report.html,execution_timeline.html,execution_trace.txtandpipeline_dag.dot/pipeline_dag.svg. - Reports generated by the pipeline:
pipeline_report.html,pipeline_report.txtandsoftware_versions.yml. Thepipeline_report*files will only be present if the--email/--email_on_failparameter’s are used when running the pipeline. - Reformatted samplesheet files used as input to the pipeline:
samplesheet.valid.csv. - Parameters used by the pipeline run:
params.json.
- Reports generated by Nextflow:
Nextflow provides excellent functionality for generating various reports relevant to the running and execution of the pipeline. This will allow you to troubleshoot errors with the running of the pipeline, and also provide you with other information such as launch commands, run times and resource usage.